These costs are constant over a specified time and the amount does not change with production output levels. In cost accounting, fixed costs can be allocated using various methods, such as absorption costing, activity-based costing (ABC), and direct costing. If a company has to pay 50,000 ₹ each month to cover the cost of the lease but does not manufacture anything during the month, the lease payment is still due for payment. These costs are not fixed for all time; they will change over time although not affect the quantity of production for the relevant period. For example, a company bears various expenses for the production of a https://ecoenergy.com.vn/new-york-tax-tables-2024-tax-rates-and-thresholds-2/ particular product and the cost paid as the rent of the warehouse is fixed for a period of the lease.

First level
A common example of a mixed cost is a utility bill, which often includes a fixed monthly service fee plus a variable charge based on consumption. A salesperson’s compensation might also be a mixed cost, consisting of a fixed monthly salary plus a commission. Step costs are fixed for a specific range of activity and then increase to a new fixed level once a threshold is surpassed. For example, if a business incurs $30,000 in fixed costs per month and produces 2,000 units, the AFC is $15 per unit ($30,000 / 2,000).
- Properly categorizing and accounting for fixed costs in the income statement ensures accurate financial reporting and aids in evaluating the business’s operational efficiency.
- When factors like sales commissions are factored into per-unit production costs, sales and production levels can impact variable costs.
- Firstly, they provide a baseline for determining the minimum level of revenue needed to cover essential expenses.
- It is a fixed cost as it is incurred with the same value over the asset’s life.
- Whether through loans, credit, or other arrangements, alternative capital sources can help to buffer against increased fixed costs and keep the business running.
Exercises and Examples for Fixed Costs
- It is also necessary for companies to consider if the revenue generated is adequate on its own to meet the total cost, fixed costs included, of the intended investment.
- With federal rates on the rise,some highly-rated student loan companies have also increased their rates.
- A fixed cost is an expense that your business must pay regularly, and it doesn’t fluctuate with the amount of goods or services you produce.
- Higher fixed costs result in a higher break-even point, requiring more sales to cover expenses.
To qualify for a private loan, you’ll need to attend an eligible school and meet the lender’s age, education or citizenship requirements, as well as credit and income criteria. Undergraduate students usually what is fixed cost need to apply with a creditworthy cosigner. Once you’ve gained approval, your lender will certify the funding amount with your college or university. You may be allowed to borrow up to 100% of your cost of attendance minus other financial aid you expect to receive. The funds are usually disbursed directly to the school, with any excess amount credited to you later.
What is Fixed Cost? Its Importance, Examples & Misconceptions
- A company’s costs classified as “fixed” are incurred periodically, so there is a set schedule and dollar amount attributable to each cost.
- Businesses and business owners are constantly faced with financial decisions that can ultimately determine the success or failure of their enterprise.
- Learn how to build, read, and use financial statements for your business so you can make more informed decisions.
- These costs do not change in the immediate future (within upcoming 1 year), regardless of the level of production or sales.
- While some fixed costs are essential, others can be reduced or eliminated through strategic decisions, such as shifting to remote work to avoid office rent.
- Private student loans can help with additional expenses not covered by financial aid.
If production increases to 3,000 units, the AFC drops to $10 per unit, and at 5,000 units, it falls further to $6 per unit. The AFC never reaches zero but consistently decreases as fixed costs are spread over a larger number of units. It means TFC remains the same whether the company produces nothing or thousands of units. By having a clear understanding of fixed costs in both pricing and budgeting, businesses can make informed decisions to drive their success. In conclusion, it’s crucial to understand and manage fixed costs in different business contexts.
Permanent full-time employees present a fixed monthly expense to your business. That’s because their salaries don’t automatically change when the company’s volume changes. For instance, increasing output using the same amount of material can dramatically cut down costs, provided the quality of goods isn’t impacted. The break-even point is the required output level for a company’s sales to equal its total costs, i.e. the inflection point where a company turns a profit.
- Examples include rent, employee salaries, insurance, and debt payments.
- While fixed costs are essential in determining profitability, managers must distinguish between recoverable and non-recoverable expenses when making strategic choices.
- By dividing its TFC by 50 — the number of units the business produced last month — the company can see its average fixed cost per unit of product.
- For example, rent is a fixed cost that may increase due to inflation or a lease term change.
- Variable costs are expenses that change when a company increases or decreases production levels.
- Some of these remain static regardless of output, while others will fluctuate.

It is vital in pricing decisions, as it helps managers set prices that cover their fixed costs and generate profits. Understanding and managing fixed costs is necessary for business owners and managers. This per-unit figure is used to determine the break-even point, which is the level of sales at which total revenues equal total costs, resulting in zero profit and zero loss. To find the break-even point in units, the formula is Total Fixed Costs divided by the Contribution Margin per Unit.

Breakeven Analysis
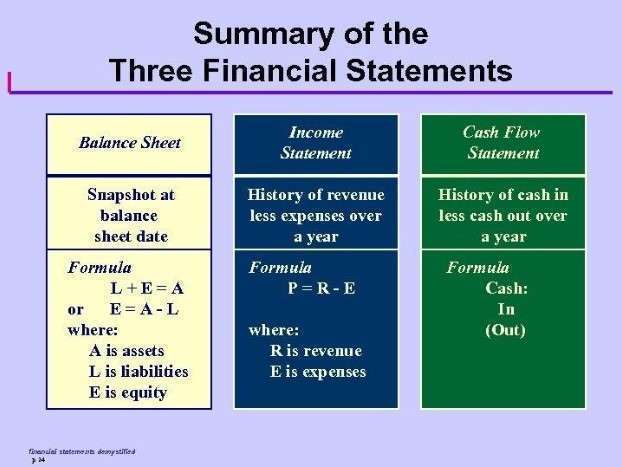
When you consider whether or not something is contracted at a specific rate and whether or not the rate of a cost fluctuates from month to month based on variables. Fixed costs are typically found on a company’s income statement under indirect or operating balance sheet expenses. Once accounted for, they appear on the company’s balance sheet and cash flow statement.